لغة إنجليزية01
Aperçu des sections
-
Name of the unit: Foreign Language
University: University of Mohamed Seddik Ben Yahia-Jijel

Faculty: Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences
Department: Sociology
Year: first year
Credit: 1
Coefficient: 1
Hourly volume during the semester: 22 hours and 30 minutes
Weekly hourly volume: 1 hour and 30 minutes (directed work)
Evaluation method: test
Teaching method: Distance and present
2. Information about the Teacher
-
-
This course aims to develop students' fundamental skills in English: listening, speaking, reading, and writing. It emphasizes vocabulary building, grammar structures,
pronunciation, and comprehension through interactive and practical methods. The goal is to help students communicate effectively in everyday and academic contexts.
Learners will gradually acquire confidence in both oral and written forms. The course also fosters autonomous learning and active language use.

-
1. Basic knowledge of the English alphabet and sounds
2. Ability to read simple English sentences
3. Familiarity with classroom instructions in English
4. Willingness to engage in language learning activities
-
The best activities for beginners are visual, interactive, and repetitive, focusing on listening and speaking with minimal pressure.
Here is a simple, effective
 activity that requires very little prior knowledge.
activity that requires very little prior knowledge.
-
-
1. Introduction to the English Alphabet and Sounds
2. Basic Greetings and Everyday Expressions
3. The Verb “To Be” and Personal Information
4. Articles, Nouns, and Plural Forms
5. Simple Present Tense and Daily Routines
6. Describing People and Places (Adjectives)
7. Prepositions of Time and Place
8. Asking and Answering Questions
9. Introduction to Reading Short Paragraphs
10. Writing Simple Sentences and Paragraphs
11. Listening and Responding to Everyday Situations
12. Speaking Practice: Dialogues and Role Plays
13. Functional Grammar: Modal Verbs (can, must, should)
14. Basic Writing Tasks: Informal Emails and Notes.

-
In the English alphabet there are 26 letters, but these letters produce 44 sounds. For this reason, one letter is used to produce more than one sound. In order to know the correct pronunciation certain symbols denoting these sounds have been devised and standardized. By learning these symbols, you will be able to find the correct pronunciation of any word in a standard dictionary. These symbols will also help you to go through the book with guidance for correct pronunciation of words and conversations. These sounds are classified into two types
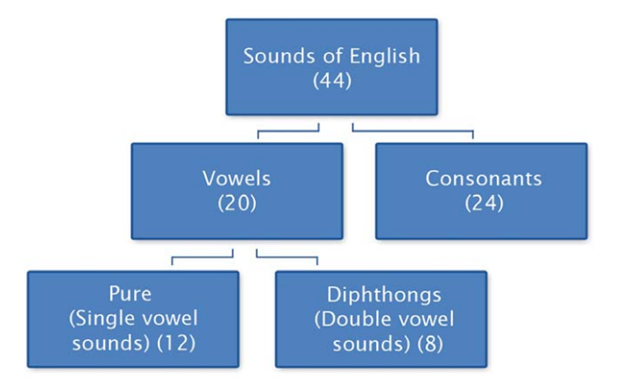 :
: -
Expression
When to Use It
Example
Hello / Hi
Any time, informal
Hi! We'd like a table for two, please."
Good morning
Before noon.
"Good morning. Is breakfast still being served?"
Good afternoon
From noon until ~5-6 PM
"Good afternoon. Can you tell me where the museum is?"
Good evening
After ~5-6 PM
"Good evening. Do you have any tickets for tonight's show?"
Goodbye / Bye
When leaving
"Bye! Thanks for a great tour!"
Have a good day!
A friendly way to end an interaction.
"Thank you! Have a good day!"
See you later
If you expect to see the person again
(To your hotel concierge) "See you later. I'll need a taxi at 7 AM."
-
The verb "to be" is the most fundamental building block of English, and it's essential for exchanging personal information, which is at the heart of tourism and travel.
Mastering the verb "to be" allows you to:
v Introduce yourself (I am...)
v State your origin (I am from...)
v Ask for locations (Where is...?)
v Describe your state (I am lost/happy/tired)
v Identify objects (This is my bag)
v What is a “to be” verb?
•A verb that is used in a number of ways in the English language, including linking, passive construction, and auxiliary
•Has many forms, including is, am, are, was, were, be, being, and been
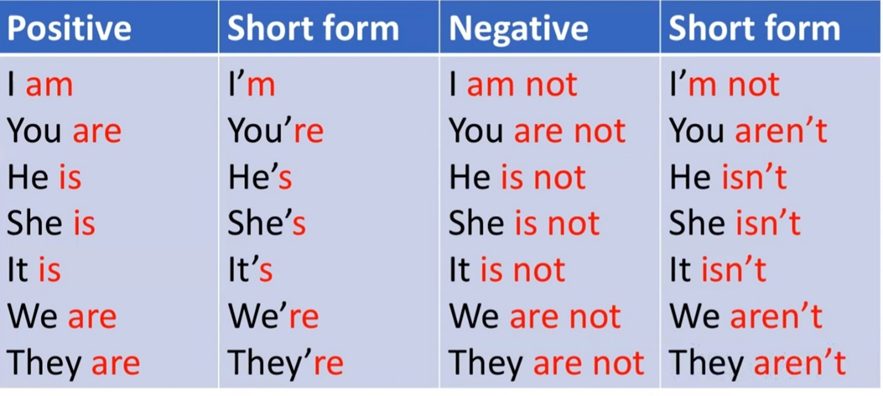
-
Personal Information

TOP QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
- What is your name?
- My name is John.
- How old are you?
- I am 25 years old.
- Where are you from?
- I am from Canada.
- What do you do?
- I am a student.
- Where do you live?
- I live in Toronto.
What is your favorite hobby
-
By understanding these basic rules, you can describe your travel experiences much more clearly and accurately:


-
-
the simple present is an English verb tense used for habits, general truths, and unchanging situations. It is formed by using the base form of the verb for most subjects (I, you, we, they), but adds an "s" for third-person singular subjects (he, she, it). Examples include "I work" and "she works," or "they live" and "he lives".
v For positive sentences, we do not normally use the auxiliary .
v 2.For the 3rd person singular (he, she, it), we add s to the main verb or es to theauxiliary.
v 3.For the verb to be , we do not use an auxiliary, even for questions and negatives
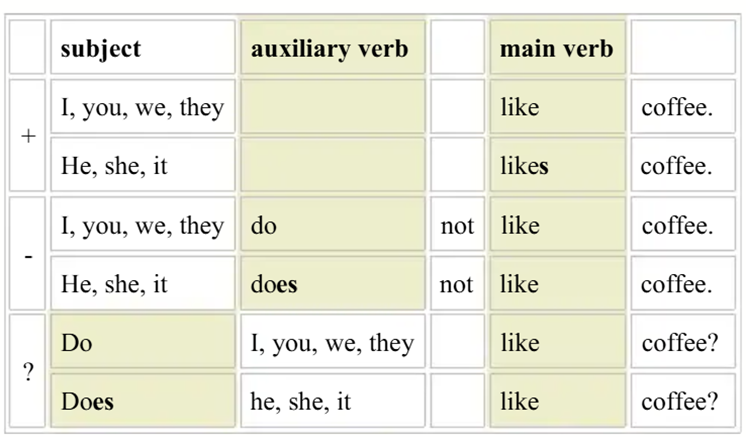
-
Look at the pictures of daily activities. Which of these activities do you do every day? Write five other activities you do every day:

You are going to read an article about the daily. Skim the text once quickly.
Underline the activities that you do in your daily routine.
I live in a village on Norway’s Atlantic coast. I get up at 7:30am and walk to college. Classes begin at 8:30am and finish at 3pm. Aft er that, I go to one of the college clubs. These are not very expensive and there are lots to choose from. I do athletics and football but you can also do things like folk dancing and cross-country skiing. When my parents come home from work, my dad makes dinner and we all eat together. Aft er that, my mum takes me out for a driving lesson. I’ve got my test soon and I need to practice!

-
Describing people and places uses adjectives to paint pictures with words, covering appearance (tall, beautiful, curly-haired) and personality (friendly, brave, intelligent) for people, and atmosphere/features (bustling, ancient, peaceful, colorful) for places, helping to add detail and feeling to writing and speech.


-
Asking and answering questions is fundamental for communication, learning, and problem-solving, involving using question words (Who, What, When, Where, Why, How) to seek information and providing relevant responses to build understanding, develop ideas, and engage with others effectively in various settings like education, reading, and daily interactions. Effective questioning requires clarity and purpose, while answering well means being direct and using complete sentences to satisfy the query.

-
Functional Grammar views modal verbs like can, must, and should as crucial tools for expressing speaker attitude (modality) such as ability, necessity, permission, possibility, and advice, modifying main verbs to add meaning beyond simple action, with can for ability/permission, must for strong obligation/deduction, and should for advice/probability, all followed by a base verb.
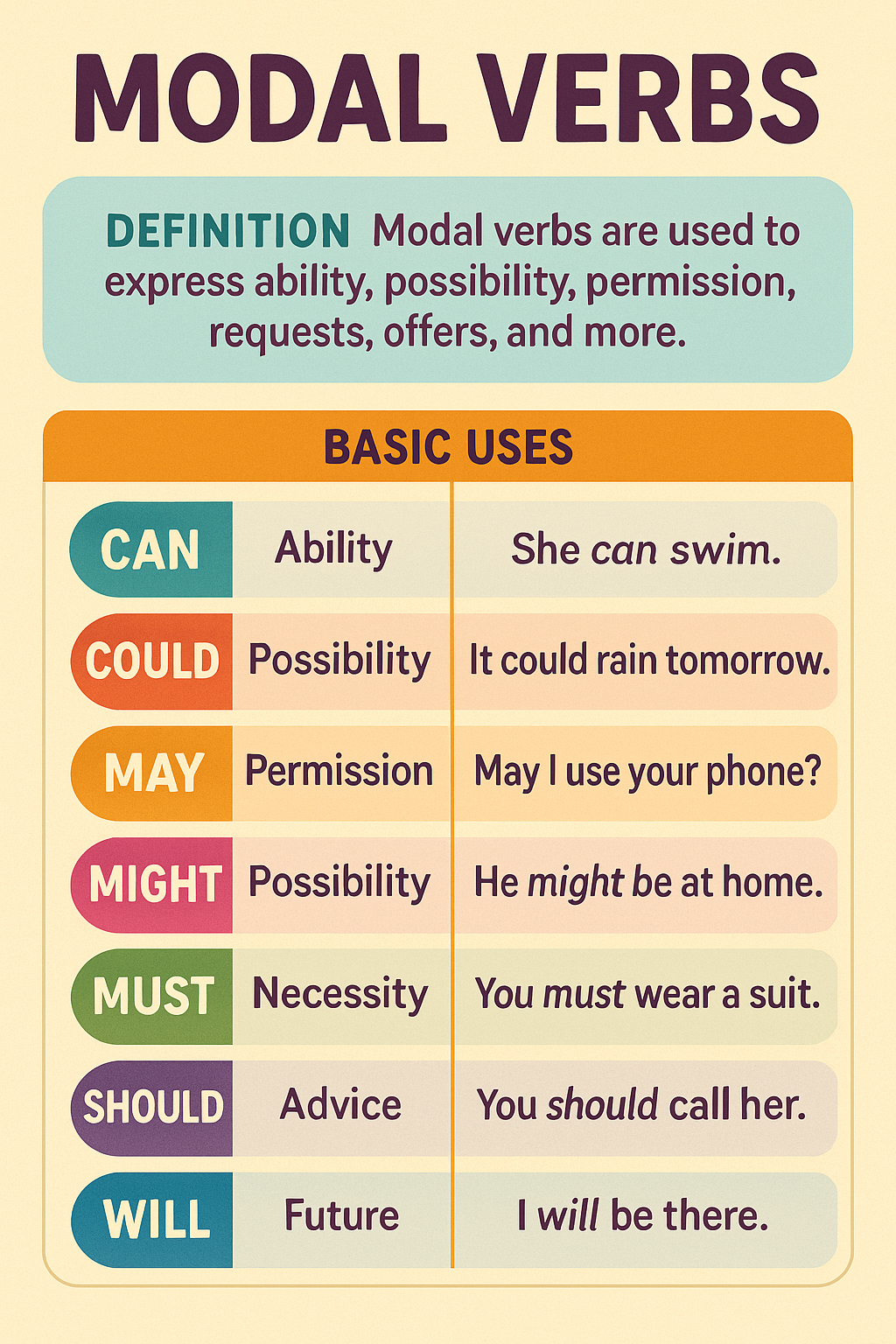
Core Functions & Examples
- Can: Ability, Permission, Possibility
- Ability: "I can swim."
- Permission: "Can I borrow your book?"
- Possibility: "It can get very hot here."
- Must: Strong Obligation, Necessity, Deduction
- Obligation: "You must finish your homework."
- Necessity: "We must leave now."
- Deduction: "She isn't here, she must be sick." (Implied strong certainty)
- Should: Advice, Recommendation, Probability/Expectation
- Advice: "You should eat more vegetables."
- Recommendation: "You should try the new restaurant."
- Probability: "He's usually on time; he should be here by now."
-
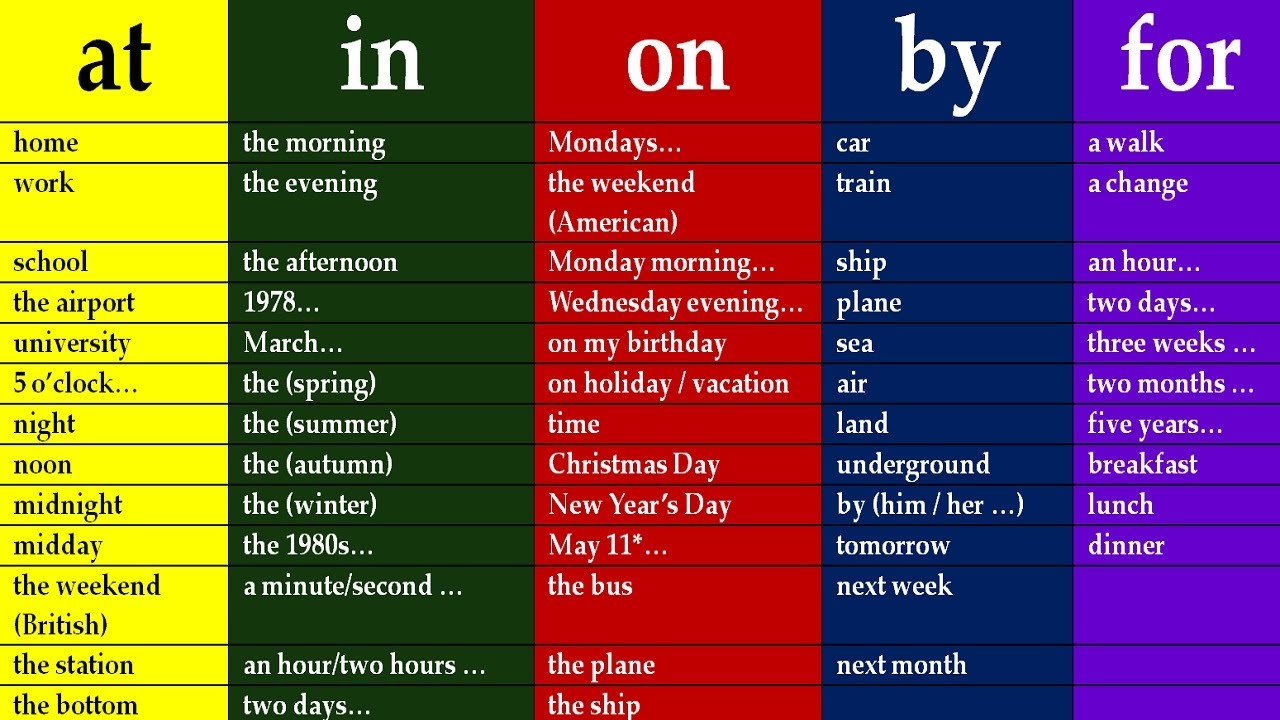
-
-
-
-
- Murphy, R. (2019). English Grammar in Use (5th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Swan, M., & Walter, C. (2014). How English Works. Oxford University Press.
- Cambridge University Press & Assessment 978-1-009-28028-0 — Mindset for IELTS Refresh with Digital Pack Foundation Student's Book Pack, https://assets.cambridge.org/97810092 /80280/excerpt/9781009280280_excerpt.pdf
- Nurma
Dhona Handayani & Frangky Silitonga(2016), EFL Students’ Ability to Identify
Singular and Plural Nouns in Paragraph, ournal of English Language, Literature,
and Teaching Volume 01, No. 2
https://ngl.cengage.com/assets/downloads/grex_pro0000000538/grex1_su3.pdf


